Reciprocity of Security Clearances
Will my security clearance transfer from one agency to another?
The answer is, maybe. It all depends on who is the ‘losing’ agency and who is the ‘gaining’ agency.

"Q" and "L" Clearances, Department of Energy
All federal agencies that grant eligibility to classified information must recognize and accept investigations and security eligibilities carried out by other branches of the federal government – provided those investigations meet the scope and standards required for the new position. Reciprocity applies to all civilian employees of the federal government, members of the military and contractors. Not only is reciprocity required by government policy, but it can save significant time and money. People will be able to start their new jobs right away and their new agencies won’t waste taxpayer dollars carrying out costly & unnecessary investigations.
For reciprocity to apply, an individual’s new position cannot require a higher eligibility than he or she currently possesses. In addition, the date of the individual’s last investigation must fall within the required timeline and the existing eligibility must not have been granted on an interim or temporary basis or by condition, deviation or waiver. Finally, if the position has Special Access Program or SAP requirements, the eligibility may be accepted reciprocally but the specific program may not be able to grant SAP access. Several policies provide more specific guidance on reciprocity within the DoD. Reciprocity for DoD Employees is outlined in DoD 5200.2-R and reciprocity for DoD Contractors is described in DoD 5220.22-M (the NISPOM).
DoD Employees
Personnel Security Investigations for DoD employees must be accepted reciprocally as long as the investigation is within scope and the employee doesn’t have a break in Military Service or Federal employment longer than 24 months.
DoD Contractors
For contractor employees, preexisting Personnel Security Clearances, or PCLs, must be accepted, provided the investigation for the PCL meets or exceeds the scope requirements for the new position, there is no new derogatory information about the employee, and eligibility was granted without condition, deviation, or waiver.
In addition to National Security Adjudications (classified access eligibility), reciprocity also applies to both HSPD-12 Common Access Card or CAC Credentialing Determinations and to Suitability & Fitness Adjudications. As established by E.O. 13467, previous suitability determinations must be accepted reciprocally, as long as they meet or exceed the suitability requirements of the new position. Requests for reciprocal acceptance of eligibility are processed at the DoD Consolidated Adjudications Facility or DOD CAF. Reciprocity requests are usually processed within two days. Eligibility Determinations for DoD employees should also be accepted, as long as there is no new derogatory information about the employee and eligibility was granted without condition, deviation or waiver.
Alignment and Reciprocity
The laws governing alignment and reciprocity come into play. Established by Executive Order 13467, alignment and reciprocity of adjudications serve to ensure fair treatment of all federal employees and prevent costly duplication of effort across agencies.
Alignment
Refers to the consistent standards and methods that are employed across all federal agencies to ensure that all federal employees receive equal treatment regardless of which agency conducts the adjudication.
Reciprocity
Reciprocity is the mutual acceptance of a suitability determination by all government agencies regardless of which agency issued the determination, as long as it meets or exceeds the suitability requirements of the new position.
Some agencies are not sure if they are required to reciprocate the clearance adjudication of another agency. However, there are various databases that agencies can utilize to determine if they are required to reciprocate the clearance adjudication of another agency, including:
- OPM’s Central Verification System (CVS)
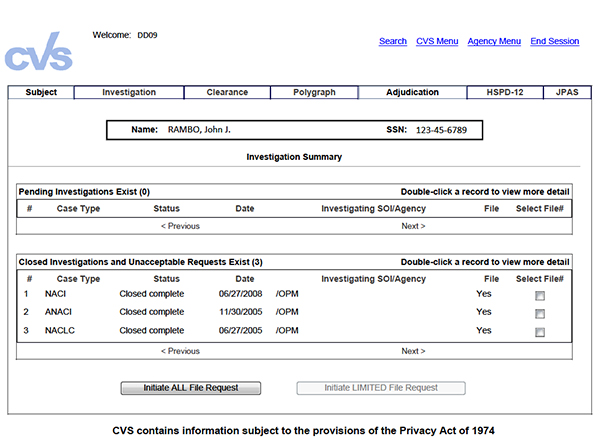
The Central Verification System, or CVS, is OPM's centralized database supporting reciprocity and information sharing within the federal government. The CVS captures and maintains information on all types of investigations and adjudications. Because multiple federal agencies use the CVS, it is key to ensuring reciprocity of previous investigations and adjudications. Receive real time clearance updates from all Investigative Service Providers (ISPs) and Central Adjudicative Facilities (CAFs) so they are always current. True reciprocity within the security community. A system that can be checked by ISPs and CAFs as part of the investigative process to determine if an individual has a current investigation and/or has ever been granted or denied a security clearance or had one revoked by any other agency of the Executive Branch. Elimination of duplicate investigations on individuals who are already cleared. Before requesting an investigation, agencies should check the Central Verification System (CVS) to determine if there is an existing adjudication or investigation that meets the current need. CVS is designated as the primary tool for facilitating reciprocal decisions, as required by Executive Orders, regulations and policies. CVS contains information on National Security, Suitability & Fitness and Homeland Security Presidential Directive 12 (HSPD-12) Personal Verification (PIV) credentialing determinations. This information is provided by agency sources, OPM legacy systems and a bridge to the Department of Defense Joint Personnel Adjudication System (JPAS). - The Department of Defense’s Joint Personnel Adjudication System (JPAS)
Repository of DOD security clearance eligibilities. JPAS= JAMS (Joint Adjudication Management System) + JCAVS (Joint Clearance & Access Verification System). JAMS is used by official government personnel such as Adjudicators. JCAVS is primarily used by industry personnel such as Facility Security Officers (FSOs). Most final security clearances are issued by Central Adjudication Facilities or CAFs. There are about 120 federal CAFs employing several hundred trained professional adjudicators. DOD personnel security staff use the personnel security automated information system, JPAS, for recording all security clearance eligibilities. - The Intelligence Community’s Scattered Castles Database
The U.S. Intelligence Community is a coalition of 17 agencies and organizations, including the ODNI, within the Executive Branch that work both independently and collaboratively to gather and analyze the intelligence necessary to conduct foreign relations and national security activities. The other 16 are Army Intelligence, Navy Intelligence, Air Force Intelligence, Marine Corps Intelligence, Coast Guard Intelligence, State, Treasury, CIA, DEA, DHS, DIA, DOE, FBI, NGA, NRO and NSA.
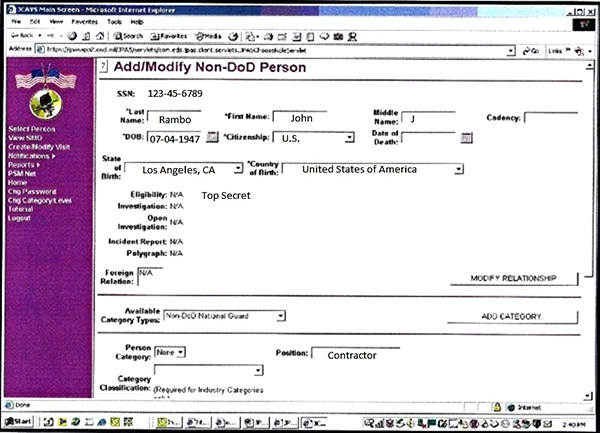

The Intelligence Community Security Clearance Repository, commonly known as Scattered Castles, is an up-to-date, authoritative source of clearance and access information on approximately 2 million IC and Department of Defense personnel. Scattered Castles is hosted as Community of Interest (COI) on the Joint Worldwide Intelligence Communications System (JWICS). The scope of the Scattered Castles Program is to provide a common, trusted repository of individuals' clearance and accesses, easily accessible by a controlled set of security professionals within the IC with a valid need to verify clearance and access information. JPAS was designed to provide the Department of Defense with a common information resource for granting and sharing personnel security eligibility determinations and recording personnel access to sensitive and non-sensitive compartmented information. JPAS is the DOD’s clearance repository. Scattered Castles serves essentially the same purpose for the Intelligence Community (IC). Scattered Castles is the clearance repository for the IC. The Scattered Castles database is the IC's authoritative personnel security repository for verifying personnel security access approvals regarding SCI and other controlled access programs. Scattered Castles is an Intelligence Community (IC) Personnel Security Database that verifies personnel security access and visit certifications. ICPG 704.5 (Signed Oct. 08) mandates the recognition, use and reciprocity of the Scattered Castles Database across all components of the IC.
What is the system of record for the Department of Defense adjudicative decisions?
The Department of Defense Joint Personnel Adjudication System (JPAS).
What is the system of record for Intelligence Community adjudicative decisions?
The Director of National Intelligence Scattered Castles Database.
Who has access to Scattered Castles?
SCI PMs – Special Security Offices have the appropriate personnel access to Scattered Castles.
Is there a point of contact (POC) for Joint Personnel Adjudication System (JPAS) and Scattered Castles that non-DOD agencies can contact?
For JPAS inquires, you may call 703-325-9495 or 703-325-6062.
For Scattered Castles inquires, you may contact the ODNI Special Security Center (SSC) Help Desk on 1-866-304-4238 or dni-ssc-help@ugov.gov.
Intelligence Community Policy Guidance
An agency can also fax an “Inter-Agency Clearance Verification Request” to the appropriate agency to determine the relevant clearance information. The request form and appropriate numbers can be found at https://opmis.xsp.org.
Directives, Executive Orders (EO) and Regulations that Mandate Reciprocity of Security Clearances in the Federal Government
Remember, reciprocity is not just a suggestion – it is a Requirement outlined in numerous government policies including several Executive Orders, the Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004, the Director of National Intelligence Memorandum, “Executive Order 13467 and Reciprocal Recognition of Existing Personnel Security Clearances,” and other policy guidance.
Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 (IRTPA) – 17 December 2004
Title III of IRTPA established statutory guidelines for reciprocity of security clearances. This act provides congressional direction that all legitimate government clearances are to be accepted and transferable between and among government agencies.
Presidential Executive Order 12968 : “ Access To Classified Information” –7 August 1995
Signed by President Clinton, this Executive Order sets eligibility standards for agency heads in granting access to National Security Information and details the investigative and adjudicative requirements for each level of access. It also defines conditions for when reciprocity must be practiced and for when conditions allow for denial of reciprocity.
Presidential Executive Order 13467: “Reforming Processes Related to Suitability for Government Employment, Fitness for Contractor Employees, and Eligibility for Access to Classified National Security Information” – 2 July 2008
Signed by President Bush, this Executive Order established the Performance Accountability Council (PAC) chaired by the Deputy Director for Management, Office of Management and Budget. The PAC ensures alignment of security and suitability investigative and adjudicative processes. This Executive Order also established the Suitability Executive Agent and the Security Executive Agent. The Director of the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) serves as the Suitability Executive Agent and the Director of National Intelligence (DNI) serves as the Security Executive Agent.
Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
Memorandums to Executive Departments and Agencies: “Reciprocal Recognition of Existing Personnel Security Clearances” -- 12 December 2005, 17 July 2006, and 14 November 2007 Signed by Clay Johnson, Deputy Director for Management, these three memorandums implemented guidance for uniform acceptance of compatible security clearances. The memorandums further clarified exceptions and introduced the Checklist of Permitted Exceptions to Reciprocity.
Director of National Intelligence Memorandum: “Executive Order 13467 and reciprocal Recognition of Existing Personnel Security Clearances” – 1 October 2008
Signed by DNI J.M. McConnell, this memorandum focused on the DNI’s commitment as Security Executive Agent, in streamlining the process by which eligibility for access to classified national security information is determined. Workforce mobility is assured by continued success of inter-agency reciprocity of security clearances. Executive Order 13467 directs reciprocal recognition while ensuring cost-effective, timely and efficient protection of the national interest.
Director of National Intelligence Community Policy Guidance 704.4 (ICPG 704.4): “Reciprocity of Personnel Security Clearance and Access Determinations” – 2 October 2008
This policy provides DNI guidance on reciprocity within the Intelligence Community (IC) and defines those areas where reciprocity must be supported by IC element heads and amplifies those special considerations and exceptions to reciprocity that apply within the IC to protect intelligence methods and sources.
Presidential Executive Order 13488
Granting Reciprocity on Excepted Service and Federal Contractor Employee Fitness and Reinvestigating Individuals in Positions of Public Trust” (16 January 2009) Aligns reciprocity between Security Clearance determinations and Public Trust determinations.